RS/tRNA Foundational Publication Support
Bryson, David I., Chenguang Fan, Li-Tao Guo, Corwin Miller, Dieter Söll, and David R. Liu. (dec) 2017. “Continuous Directed Evolution Of Aminoacyl-Trna Synthetases”. Nature Chemical Biology 13: 1253-1260. doi:10.1038/nchembio.2474.
RS/tRNA Pair Development Year
2017
ncAA(s) Incorporated
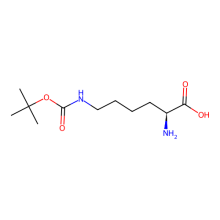
Nε-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-L-lysine (BocLys)
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
ncAA Utility
Extra-‐chromosomal array (low stability), biolistic bombardment. Scattered in different places in animal.
RS Organism of Origin
Parent RS
RS Mutations
V31I
T56P
H62Y
A100E
T56P
H62Y
A100E
tRNA Organism of Origin
Parent tRNA
tRNA Anticodon
CUA
RS/tRNA Availability
AddGene Plasmid #99222
RS/tRNA Additional Notes
The chimeric pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetase (chPylRS) species, combines residues 1–149 of Methanosarcina barkeri PylRS (MbPylRS) with residues 185–454 of M. mazei PylRS (MmPylRS). This design enhanced solubility and provided higher specific activity for L-pyrrolysine than MmPylRS alone. To evolve improved catalytic properties, commercially available Boc-lysine was used during phage-assisted continuous evolution (PACE). The four acquired mutations are in the N-terminal tRNA-binding domain, not the active site. In BL21(DE3) cells, chPylRS(IPYE) had 4-fold higher efficiency producing sfGFP with 3 ncAAs. Kinetics revealed an ~9-fold increased kcat and a 5.7-fold decreased in Km. The same four mutations installed in 6 other PylRSs improved them also.