RS/tRNA Foundational Publication Support
Mehl, Ryan A, Christopher Anderson, Stephen W Santoro, Lei Wang, Andrew B Martin, David S King, David M Horn, and Peter G Schultz. (2003) 2003. “Generation Of A Bacterium With A 21 Amino Acid Genetic Code.”. Journal Of The American Chemical Society 125 (4): 935-9.
RS/tRNA Pair Development Year
2003
ncAA(s) Incorporated
p-amino-L-phenylalanine
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
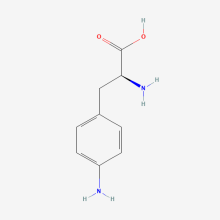
ncAA Utility
π-donating effects, hydrogen-bonding properties, and weak basicity
RS Organism of Origin
Parent RS
RS Mutations
Y32T
E107T
D158P
I159L
L162A
E107T
D158P
I159L
L162A
tRNA Organism of Origin
Parent tRNA
tRNA Anticodon
CUA
Other tRNA Mutations
C17A
U17aG
U20C
G37A
U47G
U17aG
U20C
G37A
U47G
RS/tRNA Availability
Can be obtained from AddGene: pDule #85502 (tetracyline resistance) and pDule2 #85503 (spectinomycin resistance)
RS/tRNA Additional Notes
Works with exogenously added 1 mM p-aminoPhe (pAF) or with an E coli strain containing three genes that create a pAF biosynthetic pathway. Yield of myoglobin(4) with pAF was 3 mg/L using 1 mM pAF and 1.8 mg/L using the biosynthetic pathway with a strong promoter. Wild-type was produced at 3.5 mg/L. N-terminal sequencing and MS analyses confirmed fidelity.