RS/tRNA Foundational Publication Support
Kwok, Hui Si, Oscar Vargas-Rodriguez, Sergey Melnikov V, and Dieter Söll. (2019) 2019. “Engineered Aminoacyl-Trna Synthetases With Improved Selectivity Toward Noncanonical Amino Acids.”. Acs Chemical Biology 14 (4): 603-612. doi:10.1021/acschembio.9b00088.
RS/tRNA Pair Development Year
2019
ncAA(s) Incorporated
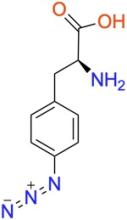
p-azido-L-phenylalanine (pAzF)
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
ncAA Utility
Used as a photocrosslinker, allowing for crosslinking and bioorthogonal click-chemistry ligation of proteins via strain-promoted cycloadditions (SPAAC) with suitably functionalized molecules.
RS Organism of Origin
Parent RS
RS Mutations
Y32L
L65V
K90Q
F108W
Q109M
D158G
I159A
I176L
R257W
E272V
L65V
K90Q
F108W
Q109M
D158G
I159A
I176L
R257W
E272V
tRNA Organism of Origin
Parent tRNA
tRNA Anticodon
CUA
Other tRNA Mutations
C17A
U17aG
U20C
G37A
U47G
U17aG
U20C
G37A
U47G
RS/tRNA Availability
n/a
Used in what cell line?
RS/tRNA Additional Notes
This RS was created as part of testing a directed evolution approach to decreasing the ncAA permissiveness (i.e. increasing the ncAA specificity) of engineered RSs. Starting with the polyspecific/pCNF-RS, selections were done to improve its specificity for pAzido-Phe. This RS has slightly better fidelity and an ~3-fold improved specificity for pAzF over pCNF, but installs pAzF slightly less efficiently than the parent RS. It is not presented as a better RS for general use, but more as proof that the directed evolution method can work as intended. Among the 4 additional mutations present ((K90Q, I176L, R257W, and E272V), it was shown that the change in specificity was largely due to the I176L mutation.