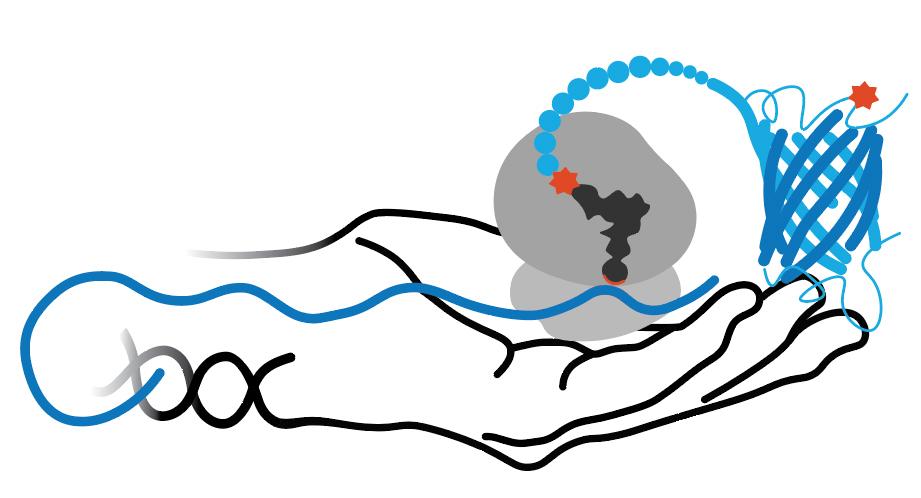
RS/tRNA Foundational Publication Support
Lang, Kathrin, Lloyd Davis, Stephen Wallace, Mohan Mahesh, Daniel J Cox, Melissa L Blackman, Joseph M Fox, and Jason W Chin. (2012) 2012. “Genetic Encoding Of Bicyclononynes And Trans-Cyclooctenes For Site-Specific Protein Labeling In Vitro And In Live Mammalian Cells Via Rapid Fluorogenic Diels-Alder Reactions.”. Journal Of The American Chemical Society 134 (25): 10317-20. doi:10.1021/ja302832g.
RS/tRNA Pair Development Year
2012
ncAA(s) Incorporated
endo-BCN-L-Lysine
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
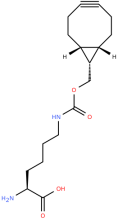
ncAA Utility
Reactive handle for SPAAC
Nε-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-L-lysine (BocLys)
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
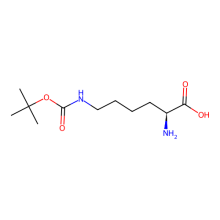
ncAA Utility
Extra-‐chromosomal array (low stability), biolistic bombardment. Scattered in different places in animal.
RS Organism of Origin
Parent RS
RS Mutations
Y271M
L274G
C313A
L274G
C313A
tRNA Organism of Origin
Parent tRNA
tRNA Anticodon
CUA
RS/tRNA Availability
n/a
RS/tRNA Additional Notes
In E.coli, produced 6-12 mg/L sfGFP(150) with fidelity verified by MS and reactivity with tetrazines. Also incorporated a closely related ncAA with a TCO ring.
In HEK-293 cells, ncAAs were incorporated into an mCherry-eGFP construct, position 128 of the EGF receptor, and the nuclear protein jun in a jun-mCherry construct. Both extracellular and nuclear proteins reacted with a tetrazine label.
In HEK-293 cells, ncAAs were incorporated into an mCherry-eGFP construct, position 128 of the EGF receptor, and the nuclear protein jun in a jun-mCherry construct. Both extracellular and nuclear proteins reacted with a tetrazine label.