RS/tRNA Foundational Publication Support
Takimoto, Jeffrey K, Katrina Adams, Zheng Xiang, and Lei Wang. (2009) 2009. “Improving Orthogonal Trna-Synthetase Recognition For Efficient Unnatural Amino Acid Incorporation And Application In Mammalian Cells.”. Molecular Biosystems 5 (9): 931-4. doi:10.1039/b904228h.
Seidel, Lisa, Barbara Zarzycka, Saheem Zaidi, Vsevolod Katritch, and Irene Coin. (2017) 2017. “Structural Insight Into The Activation Of A Class B G-Protein-Coupled Receptor By Peptide Hormones In Live Human Cells.”. Elife 6. doi:10.7554/eLife.27711.
Chin, Jason W, Ashton Cropp, Christopher Anderson, Mridul Mukherji, Zhiwen Zhang, and Peter G Schultz. (2003) 2003. “An Expanded Eukaryotic Genetic Code.”. Science (New York, N.y.) 301 (5635): 964-7.
RS/tRNA Protocols and Structural Information
Serfling, R, and I Coin. (2016) 2016. “Incorporation Of Unnatural Amino Acids Into Proteins Expressed In Mammalian Cells.”. Methods In Enzymology 580: 89-107. doi:10.1016/bs.mie.2016.05.003.
RS/tRNA Usage Publications
Coin, Irene, Vsevolod Katritch, Tingting Sun, Zheng Xiang, Fai Siu, Michael Beyermann, Raymond C Stevens, and Lei Wang. (2013) 2013. “Genetically Encoded Chemical Probes In Cells Reveal The Binding Path Of Urocortin-I To Crf Class B Gpcr.”. Cell 155 (6): 1258-69. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.008.
RS/tRNA Pair Development Year
2009
ncAA(s) Incorporated
p-azido-L-phenylalanine (pAzF)
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
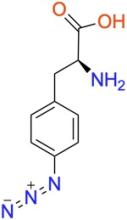
ncAA Utility
Used as a photocrosslinker, allowing for crosslinking and bioorthogonal ligation of protein.
RS Organism of Origin
Parent RS
RS Mutations
Y37L
D182S
F183M
L186A
D265R
D182S
F183M
L186A
D265R
tRNA Organism of Origin
Parent tRNA
tRNA Anticodon
CUA
Multiple tRNAs?
Shown in 2002 paper to function better in mammalian cells when paired with the B. stearothermophilis suppressor tRNA-Tyr and this is used in plasmid available from Addgene
RS/tRNA Availability
AddGene Plasmid #105829 encodes EAziRS and the B. stearothermophylus tRNA.
RS/tRNA Additional Notes
2009 foundational paper added the D265R mutation to the RS reported as p-azidoPheRS-1 in 2003 foundational paper by Chin et al (2003) and as pAZ-EcRS1 by 2003 foundational paper by Dieters et al.. The The D265R mutation in E coli Tyr RS improves its recognition of the CUA anticodon. The "E" in the RS name means "enhanced." In HeLa cells it nearly doubled the fluorescence of produced GFP(39) with pAzPhe and also improved yields with three other ncAAs. In HEK293T cells, 1 mM pAzPhe was incorporated into sites 87, 92 and 125 of GST showed increased yield and photocrosslinking of 30-100% of the protein.
This Addgene plasmid with this RS was developed in the 2017 foundational paper seems to be the current go to system for mammalian cell studies with pAzPhe. It seems this same RS was also called E2AziRS.
One oddity is that the 2009 paper reports the RS they studied as having an F183A mutation rather than the F183M mutation noted in the Addgene deposition The F183A is present in p-azidoPheRS-3 from the 2003 papers.
This Addgene plasmid with this RS was developed in the 2017 foundational paper seems to be the current go to system for mammalian cell studies with pAzPhe. It seems this same RS was also called E2AziRS.
One oddity is that the 2009 paper reports the RS they studied as having an F183A mutation rather than the F183M mutation noted in the Addgene deposition The F183A is present in p-azidoPheRS-3 from the 2003 papers.