RS/tRNA Foundational Publication Support
Zhu, Phillip, Stanislau Stanisheuski, Rachel Franklin, Amber Vogel, Cat Hoang Vesely, Patrick Reardon, Nikolai N Sluchanko, et al. (2023) 2023. “Autonomous Synthesis Of Functional, Permanently Phosphorylated Proteins For Defining The Interactome Of Monomeric 14-3-3Ζ.”. Acs Central Science 9 (4): 816-835. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.3c00191.
Park, Hee-Sung, Michael J Hohn, Takuya Umehara, Li-Tao Guo, Edith M Osborne, Jack Benner, Christopher J Noren, Jesse Rinehart, and Dieter Söll. (2011) 2011. “Expanding The Genetic Code Of Escherichia Coli With Phosphoserine.”. Science (New York, N.y.) 333 (6046): 1151-4. doi:10.1126/science.1207203.
Rogerson, D. T., A. Sachdeva, K. Wang, T. Haq, A. Kazlauskaite, S. M. Hancock, N. Huguenin-Dezot, M. M. K. Muqit, A. M. Fry, and R. Bayliss. n.d. “Efficient Genetic Encoding Of Phosphoserine And Its Nonhydrolyzable Analog” 11: 496+.
Zhang, Michael Shaofei, Simon F Brunner, Nicolas Huguenin-Dezot, Alexandria D Liang, Wolfgang H Schmied, Daniel T Rogerson, and Jason W Chin. (2017) 2017. “Biosynthesis And Genetic Encoding Of Phosphothreonine Through Parallel Selection And Deep Sequencing.”. Nature Methods 14 (7): 729-736. doi:10.1038/nmeth.4302.
RS/tRNA Protocols and Structural Information
Zhu, Phillip, Ryan A Mehl, and Richard B Cooley. (2023) 2023. “Biosynthesis And Genetic Encoding Of Non-Hydrolyzable Phosphoserine Into Recombinant Proteins In Escherichia Coli.”. Bio-Protocol 13 (21): e4861. doi:10.21769/BioProtoc.4861.
RS/tRNA Pair Development Year
2023
ncAA(s) Incorporated
2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid (nhpSer)
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
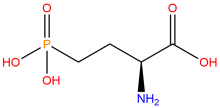
ncAA Utility
Used to produce proteins that mimic site-specific phosphorylation at a serine residue - where the phosphate group cannot by hydrolyzed - via genetic code expansion versus other protein phosphorylation strategies.
RS Organism of Origin
Parent RS
RS Mutations
E412P
E414F
P495M
I496W
F529S
E414F
P495M
I496W
F529S
tRNA Organism of Origin
Parent tRNA
tRNA Anticodon
CUA
Other tRNA Mutations
C2U
G4C
G6C
G29A
A31U
G34C
C35U
G37A
U39A
C40U
C41U
C67G
C69G
G71A
G4C
G6C
G29A
A31U
G34C
C35U
G37A
U39A
C40U
C41U
C67G
C69G
G71A
RS/tRNA Availability
Entire kit for the "PermaPhos" system (nhpSer incorporation using GCE) available as Addgene kit #1000000226.
Component Addgene IDs are:
201922 - machinery plasmid, including RS/tRNA pair
174075 and 174076 - plasmids for control sfGFP forms which can also be used for other POI
201923 - plasmid for Frb pathway
197656 - E. coli strain BL21(DE3) ΔserC
Component Addgene IDs are:
201922 - machinery plasmid, including RS/tRNA pair
174075 and 174076 - plasmids for control sfGFP forms which can also be used for other POI
201923 - plasmid for Frb pathway
197656 - E. coli strain BL21(DE3) ΔserC
Used in what cell line?
RS/tRNA Additional Notes
Using this RS/tRNA pair for nhpSer incorporation along with a biosynthetic path nhpSer was reported by Zhu et al. (2023). However the GCE tools SepRS2, Sep-tRNA-v2, and EF-Sep (a variant of EF-Tu) were developed in foundational 2015 and 2017 and 2011 papers, respectively. To work well with nhpSer it is essential to include a plasmid that encodes enzymes from the Frb pathway that lead to the endogenous biosynthesis of nhpSer.
Single and double high-fidelity nhpSer incorporation into sfGFP (site 150) yielded ∼120 and 30 mg/L culture, respectively, corresponding to efficiencies of ~40% and 13%. This is ~40-fold higher than nhpSer incorporation using exogenous 2 mM nhpSer as opposed to the endogenous biosynthesis.
Single and double high-fidelity nhpSer incorporation into sfGFP (site 150) yielded ∼120 and 30 mg/L culture, respectively, corresponding to efficiencies of ~40% and 13%. This is ~40-fold higher than nhpSer incorporation using exogenous 2 mM nhpSer as opposed to the endogenous biosynthesis.