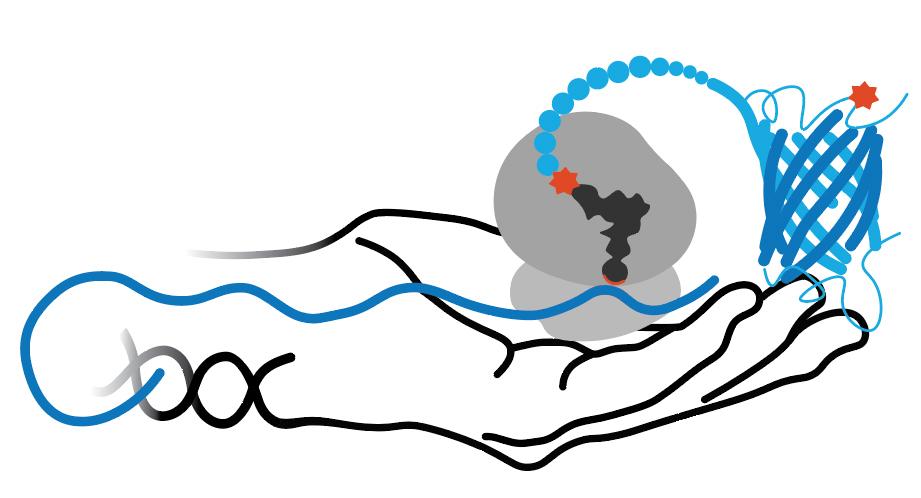
RS/tRNA Foundational Publication Support
Yanagisawa, Tatsuo, Ryohei Ishii, Ryuya Fukunaga, Takatsugu Kobayashi, Kensaku Sakamoto, and Shigeyuki Yokoyama. (2008) 2008. “Multistep Engineering Of Pyrrolysyl-Trna Synthetase To Genetically Encode N(Epsilon)-(O-Azidobenzyloxycarbonyl) Lysine For Site-Specific Protein Modification.”. Chemistry & Biology 15 (11): 1187-97. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.10.004.
Peng, Tao, and Howard C Hang. (2016) 2016. “Site-Specific Bioorthogonal Labeling For Fluorescence Imaging Of Intracellular Proteins In Living Cells.”. Journal Of The American Chemical Society 138 (43): 14423-14433.
Yanagisawa, Tatsuo, Nobumasa Hino, Fumie Iraha, Takahito Mukai, Kensaku Sakamoto, and Shigeyuki Yokoyama. (2012) 2012. “Wide-Range Protein Photo-Crosslinking Achieved By A Genetically Encoded N(Ε)-(Benzyloxycarbonyl)Lysine Derivative With A Diazirinyl Moiety.”. Molecular Biosystems 8 (4): 1131-5. doi:10.1039/c2mb05321g.
Milles, Sigrid, Swati Tyagi, Niccolò Banterle, Christine Koehler, Virginia VanDelinder, Tilman Plass, Adrian P Neal, and Edward A Lemke. (2012) 2012. “Click Strategies For Single-Molecule Protein Fluorescence.”. Journal Of The American Chemical Society 134 (11): 5187-95. doi:10.1021/ja210587q.
Nikić, Ivana, Gemma Estrada Girona, Jun Hee Kang, Giulia Paci, Sofya Mikhaleva, Christine Koehler, Nataliia Shymanska V, Camilla Ventura Santos, Daniel Spitz, and Edward A Lemke. (2016) 2016. “Debugging Eukaryotic Genetic Code Expansion For Site-Specific Click-Paint Super-Resolution Microscopy.”. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. In English) 55 (52): 16172-16176. doi:10.1002/anie.201608284.
Arsić, Aleksandra, Cathleen Hagemann, Nevena Stajković, Timm Schubert, and Ivana Nikić-Spiegel. (2022) 2022. “Minimal Genetically Encoded Tags For Fluorescent Protein Labeling In Living Neurons.”. Nature Communications 13 (1): 314. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-27956-y.
Schmidt, Moritz J, and Daniel Summerer. (2013) 2013. “Red-Light-Controlled Protein-Rna Crosslinking With A Genetically Encoded Furan.”. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. In English) 52 (17): 4690-3. doi:10.1002/anie.201300754.
Serfling, Robert, Christian Lorenz, Maja Etzel, Gerda Schicht, Thore Böttke, Mario Mörl, and Irene Coin. (2018) 2018. “Designer Trnas For Efficient Incorporation Of Non-Canonical Amino Acids By The Pyrrolysine System In Mammalian Cells.”. Nucleic Acids Research 46 (1): 1-10. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx1156.
Plass, Tilman, Sigrid Milles, Christine Koehler, Carsten Schultz, and Edward A Lemke. (2011) 2011. “Genetically Encoded Copper-Free Click Chemistry.”. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. In English) 50 (17): 3878-81. doi:10.1002/anie.201008178.
Hoffmann, Jan-Erik, Tilman Plass, Ivana Nikić, Iker Valle Aramburu, Christine Koehler, Hartmut Gillandt, Edward A Lemke, and Carsten Schultz. (2015) 2015. “Highly Stable Trans-Cyclooctene Amino Acids For Live-Cell Labeling.”. Chemistry (Weinheim An Der Bergstrasse, Germany) 21 (35): 12266-70. doi:10.1002/chem.201501647.
RS/tRNA Protocols and Structural Information
Hino, Nobumasa, Kensaku Sakamoto, and Shigeyuki Yokoyama. (2012) 2012. “Site-Specific Incorporation Of Unnatural Amino Acids Into Proteins In Mammalian Cells.”. Methods In Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.j.) 794: 215-28. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-331-8_13.
Nikić, Ivana, Jun Hee Kang, Gemma Estrada Girona, Iker Valle Aramburu, and Edward A Lemke. (2015) 2015. “Labeling Proteins On Live Mammalian Cells Using Click Chemistry.”. Nature Protocols 10 (5): 780-91. doi:10.1038/nprot.2015.045.
Yanagisawa, Tatsuo, Mitsuo Kuratani, Eiko Seki, Nobumasa Hino, Kensaku Sakamoto, and Shigeyuki Yokoyama. (2019) 2019. “Structural Basis For Genetic-Code Expansion With Bulky Lysine Derivatives By An Engineered Pyrrolysyl-Trna Synthetase.”. Cell Chemical Biology 26 (7): 936-949.e13. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.03.008.
RS/tRNA Usage Publications
Spence, Jennifer S, Ruina He, Hans-Heinrich Hoffmann, Tandrila Das, Emmanuelle Thinon, Charles M Rice, Tao Peng, Kartik Chandran, and Howard C Hang. (2019) 2019. “Ifitm3 Directly Engages And Shuttles Incoming Virus Particles To Lysosomes.”. Nature Chemical Biology 15 (3): 259-268. doi:10.1038/s41589-018-0213-2.
Meineke, Birthe, Johannes Heimgärtner, Lorenzo Lafranchi, and Simon J Elsässer. (2018) 2018. “Methanomethylophilus Alvus Mx1201 Provides Basis For Mutual Orthogonal Pyrrolysyl Trna/Aminoacyl-Trna Synthetase Pairs In Mammalian Cells.”. Acs Chemical Biology 13 (11): 3087-3096. doi:10.1021/acschembio.8b00571.
Schloßhauer, Jeffrey L, Anne Zemella, Srujan K Dondapati, Lena Thoring, Manpreet Meyer, and Stefan Kubick. (2023) 2023. “Enhancing The Performance Of A Mutant Pyrrolysyl-Trna Synthetase To Create A Highly Versatile Eukaryotic Cell-Free Protein Synthesis Tool.”. Scientific Reports 13 (1): 15236. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-42198-8.
Streit, Marcel, Mareike Hemberger, Stephanie Häfner, Felix Knote, Tobias Langenhan, and Gerti Beliu. (2023) 2023. “Optimized Genetic Code Expansion Technology For Time-Dependent Induction Of Adhesion Gpcr-Ligand Engagement.”. Protein Science : A Publication Of The Protein Society 32 (4): e4614. doi:10.1002/pro.4614.
Latorraca, Naomi R, Sam Sabaat, Chris Habrian, Julia Bleier, Cherise Stanley, Susan Marqusee, and Ehud Y Isacoff. (2024) 2024. “Domain Coupling In Activation Of A Family C Gpcr.”. Biorxiv : The Preprint Server For Biology. doi:10.1101/2024.02.28.582567.
Nikić, Ivana, Tilman Plass, Oliver Schraidt, Jędrzej Szymański, John A G Briggs, Carsten Schultz, and Edward A Lemke. (2014) 2014. “Minimal Tags For Rapid Dual-Color Live-Cell Labeling And Super-Resolution Microscopy.”. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. In English) 53 (8): 2245-9. doi:10.1002/anie.201309847.
Schmidt, Moritz J, Julia Borbas, Malte Drescher, and Daniel Summerer. (2014) 2014. “A Genetically Encoded Spin Label For Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Distance Measurements.”. Journal Of The American Chemical Society 136 (4): 1238-41. doi:10.1021/ja411535q.
Mitrovich, Margaret, and Michael Vahey. (2025) 2025. “Genetically Recoding Respiratory Syncytial Virus To Visualize Nucleoprotein Dynamics And Virion Assembly.”. Acs Infectious Diseases 11 (1): 95-103. doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00321.
RS/tRNA Pair Development Year
2008
ncAA(s) Incorporated
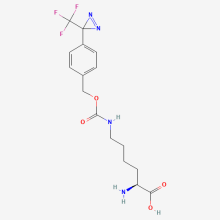
Nε-(o Azidobenzyloxycarbon yl)-L-lysine (AzZLys)
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
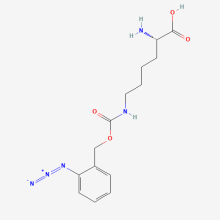
ncAA Utility
Reactive handle for Staudinger ligation
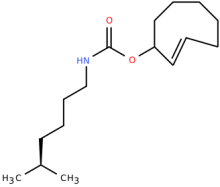
N6-(Benzyloxycarbonyl)-L-lysine (Z-Lys)
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
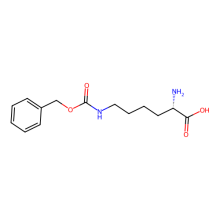
ncAA Utility
n/a
4'-TCOK (TCO)
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
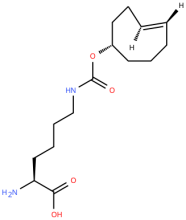
ncAA Utility
Reactive handle for IEDDA.
endo-BCN-L-Lysine
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
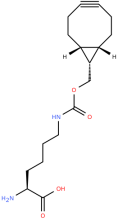
ncAA Utility
Reactive handle for SPAAC
exoBCN-L-Lysine
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
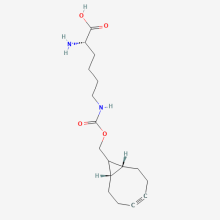
ncAA Utility
Reactive handle for SPAAC
2'-axialTCOK (TCO*)
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
ncAA Utility
Biorthogonal ligation, Click-Chemistry
TmdZLys
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
ncAA Utility
Photo-cross-linking agent, and head to head comparison with Bpa and TmdPhe showed that TmdZLys led to successful crosslinking from more positions including those further apart, up to 15 Å. Tests were done with the GRB2 protein crosslinking with both the EGF receptor and the SHC receptor protein.
pNO2ZLys
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
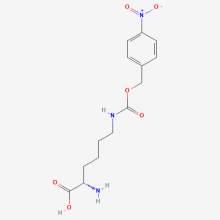
ncAA Utility
Photo-cross-linking agent, but no tests were done on this ncAA in the founding paper. Crosslinking experiments were only done with TmdZLys
N6-[2-(furan-2-yl)ethoxy]carbonyl Lys
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
![(2S)-2-amino-6-[2-(furan-2-yl)ethoxycarbonylamino]hexanoic acid](/sites/gce4all/files/styles/medium/public/2025-01/Page_29_Structure_2.png?itok=lSSQ9Ih2)
ncAA Utility
Reactive handle for cross-linking DNA with red light
2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-pyrrolin-1-oxyl
ncAA Structure (png, jpg, jpeg)
![3-[[[[[(5S)-5-Amino-5-carboxypentyl]amino]carbonyl]oxy]methyl]-2,5-dihydro-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-1H-pyrrol-1-yloxy](/sites/gce4all/files/styles/medium/public/2025-01/Page_29_Structure_1.png?itok=rcllRQAQ)
ncAA Utility
n/a
RS Organism of Origin
Parent RS
RS Mutations
Y306A
Y384F
Y384F
tRNA Organism of Origin
Parent tRNA
tRNA Anticodon
CUA
Multiple tRNAs?
Serfling et al 2018 paper on "Designer tRNAs ..." creates 2 modified tRNA-Pyl variants to perform better in mammalian cells, the "M15", and "C15" variants. Later paper on optimizing mammalian expression paired the "M15" variant with this RS.
RS/tRNA Availability
Also called MmPylRS-AF or just PylRS-AF
Available in multiple Addgene Plasmids
#122650 (mammalian - from 2019 Spence et al application citing 2016 TCOK work; Hang group )
#223511 (E coli - from 2012 Milles at al work)
#223508 (mammalian - with nuclear export signal (NES); from 2016 Nikic et al work)
#182287 and #182653 (mammalian - with NES and codon optimized; from 2022 Arsic et al paper)
#174902 (mammalian with NES from Elsasser group)
#196486 (mammalian from Sakamoto group)
Available in multiple Addgene Plasmids
#122650 (mammalian - from 2019 Spence et al application citing 2016 TCOK work; Hang group )
#223511 (E coli - from 2012 Milles at al work)
#223508 (mammalian - with nuclear export signal (NES); from 2016 Nikic et al work)
#182287 and #182653 (mammalian - with NES and codon optimized; from 2022 Arsic et al paper)
#174902 (mammalian with NES from Elsasser group)
#196486 (mammalian from Sakamoto group)
RS/tRNA Additional Notes
Original 2008 paper included crystal structures. Y384F mutant was selected to work with ZLys and Y306A change was rationally added to improve performance. Using 1 mM AzZLys produced >10 mg/L GST with ncAA at residue 25 protein, verified incorporation with MS, and success with Staudinger ligation to attach a fluorescent label.
2013 paper working with Furans allowed for 17mg/L yield of GFP-Y39 in the presence of the Furanyl Lysine ncAA, with no yield in its absence, confirmed by ESI MS. Additionally, was used to express Thioredoxin at position R74 in E. coli with a yield of 14mg/L purified Thioredoxin, confirmed by ESI MS.
2016 paper showed RS is permissive for exo-BCNK, endo-BCNK and 2'-aTCOK, and showed mammalian cell incorporation into sfGFP residue 39 and interferon-inducible transmembrane protein 3 residue 8. UP50 for 2'-aTCOK was ~10 microM. incorporated ncAA could be labeled with tetrazine flurophore.
2013 paper working with Furans allowed for 17mg/L yield of GFP-Y39 in the presence of the Furanyl Lysine ncAA, with no yield in its absence, confirmed by ESI MS. Additionally, was used to express Thioredoxin at position R74 in E. coli with a yield of 14mg/L purified Thioredoxin, confirmed by ESI MS.
2016 paper showed RS is permissive for exo-BCNK, endo-BCNK and 2'-aTCOK, and showed mammalian cell incorporation into sfGFP residue 39 and interferon-inducible transmembrane protein 3 residue 8. UP50 for 2'-aTCOK was ~10 microM. incorporated ncAA could be labeled with tetrazine flurophore.