ncAA Database
Displaying 1 - 25 of 56 results
| ncAA Name | ncAA Structure | ncAA Utility | Moderation State |
|---|---|---|---|
| p-acetyl-L-phenylalanine | 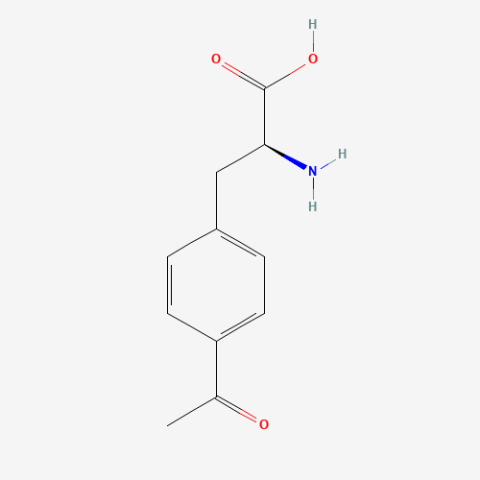
|
Site-directed spin labeling, electron paramagnetic resonance | Published: Under Review |
| (3-(3-Methyl-3H diazirine-3-yl)-propaminocarbonyl- Nε-L-lysine ( DiZPK) | 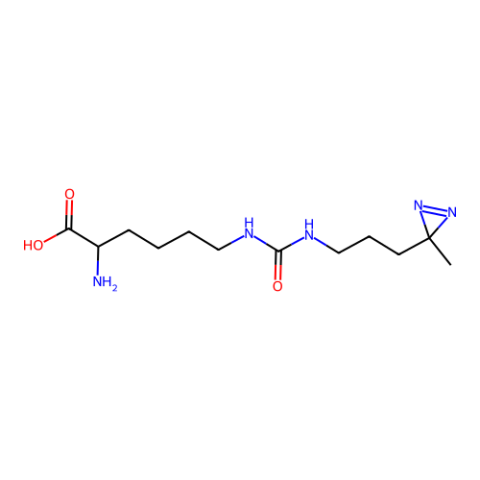
|
Photo-crosslinker | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| (S)-2-(4-Pentenyl)glycine | 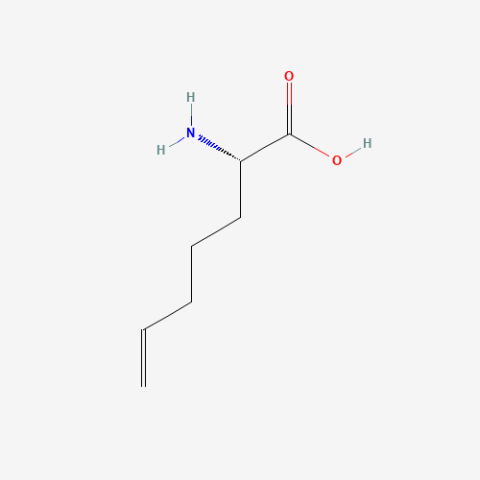
|
oxidation resistant analogue of S-Allylcysteine | Published: Under Review |
| 2'-axialTCOK (TCO*) | 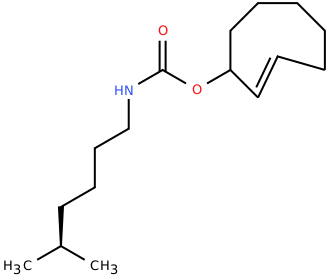
|
Biorthogonal ligation, Click-Chemistry | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| 2-Amino-3-but-2-enoxypropanoic acid | 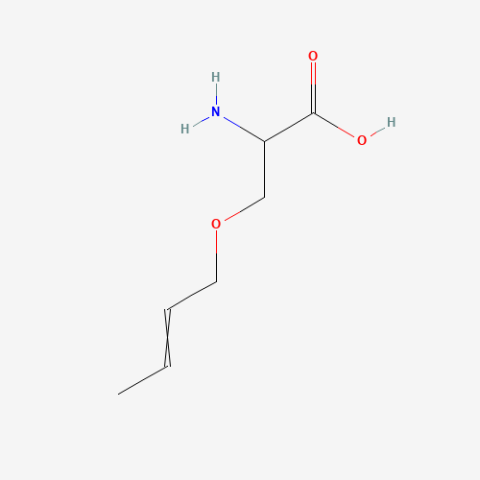
|
oxidation resistant analogue of S-Allylcysteine | Published: Under Review |
| 2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid (nhpSer) | 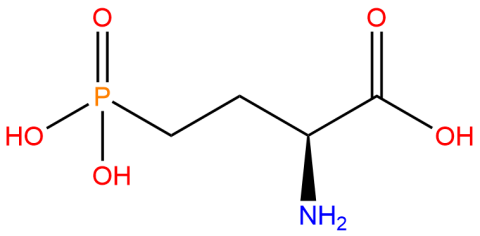
|
Used to produce proteins that mimic site-specific phosphorylation at a serine residue - where the phosphate group cannot by hydrolyzed - via genetic code expansion versus other protein phosphorylation strategies. | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| 2-Amino-7-octenoic acid | 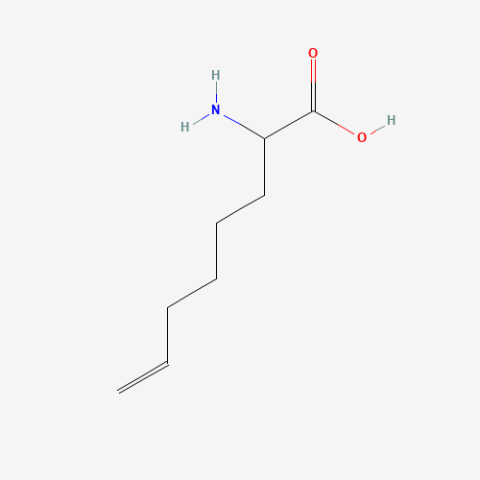
|
oxidation resistant analogue of S-Allylcysteine | Published: Under Review |
| 2-Aminooctanoate | 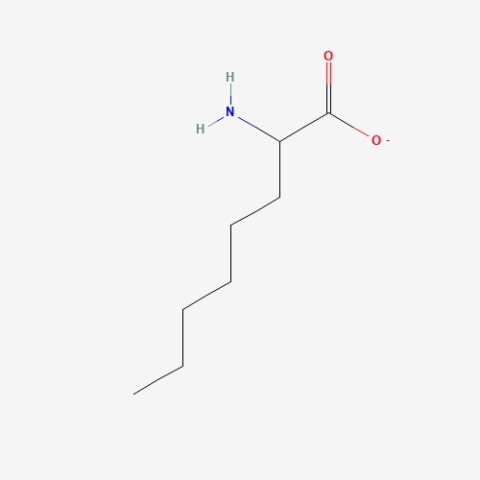
|
n/a | Published: Under Review |
| 3-(2-Naphthyl)-L-alanine | 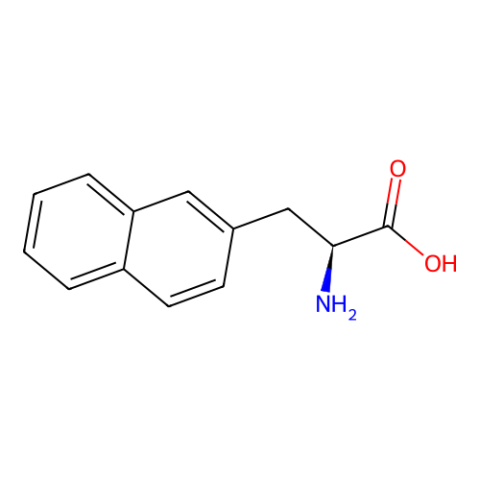
|
Speculated novel stacking properties |
Published: Under Review |
| 3-acetyl-L-phenylalanine | 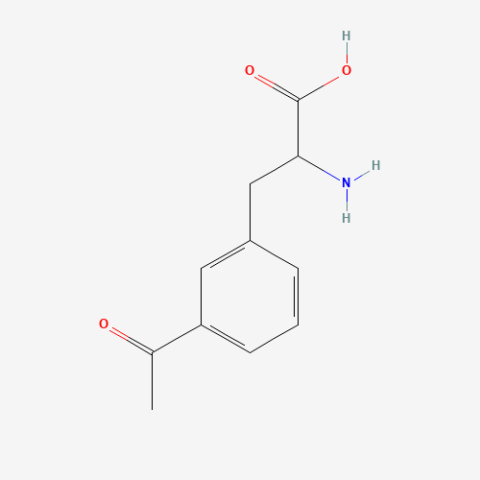
|
can be used for protein ligation | Published: Under Review |
| 3-allyl-L-phenylalanine | 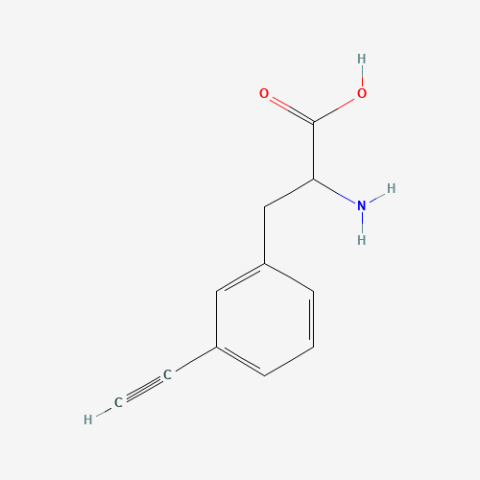
|
useful for protein ligations | Published: Under Review |
| 3-iodo-L-tyrosine | 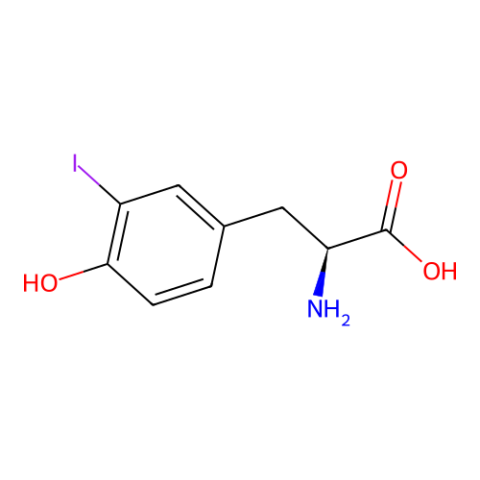
|
for anomalous dispersion phasing in protein crystallography. | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| 3-nitro-L-phenylalanine | 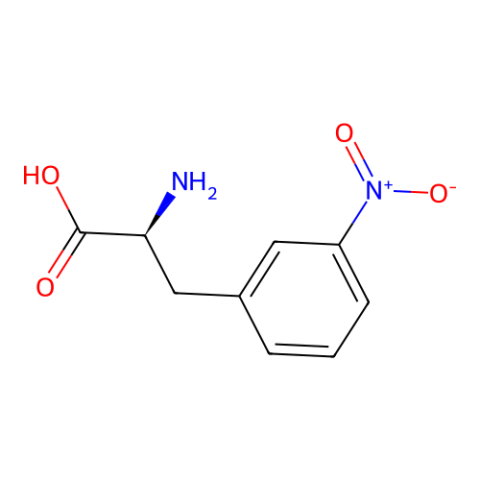
|
can quench Trp fluoresence via FRET in a distance dependent manner. May also be useful as a control for use in studies of the roles of 3-nitroTyr in protein structure-function. | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| 3-nitro-L-tyrosine | 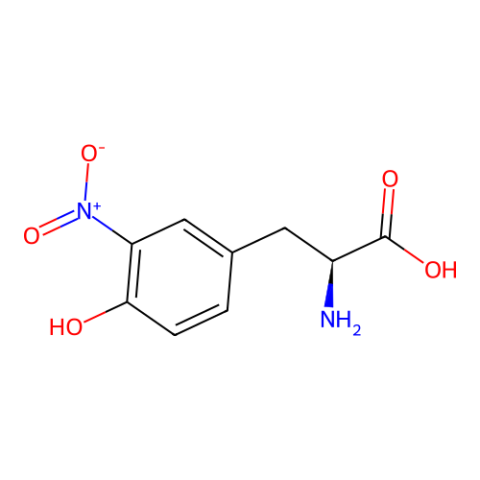
|
3-nitroTyr is a natural post-translational modification of proteins typically resulting from protein oxidation by peroxynitrite. It increases in many diseases and with age. Still unknown is if it can be reversed (by a denitrase) and if it has has a purposeful signaling role, or if it is only a modification associated with pathologies. It is known in some cases to contribute to disease pathology, but in most cases it is unknown how much it causes pathology vs. being a consequence of pathology. The ability to site specifically and quantitatively place 3-nitroTyr in positions in proteins that have been seen to occur in association with disease is a key tool to answer questions about its possible roles in normal physiology and disease. | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| 4'-TCOK (TCO) | 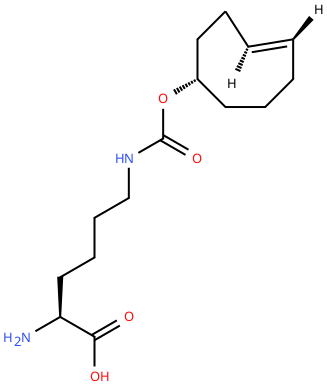
|
Reactive handle for IEDDA. | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| acridonylalanine | 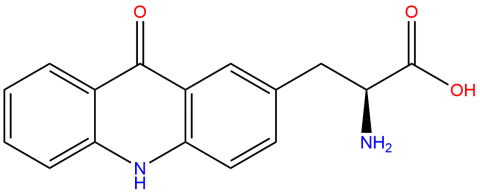
|
It is a blue-wavelength fluorescent probe used for monitoring conformational changes and other molecular dynamics in proteins. The 2013 and 2021 foundational publications provide information on its properties, and a 2023 paper (doi: 10.1002/pro.4633) provides examples of its use in FRET studies. | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| Anap (ANAP) | 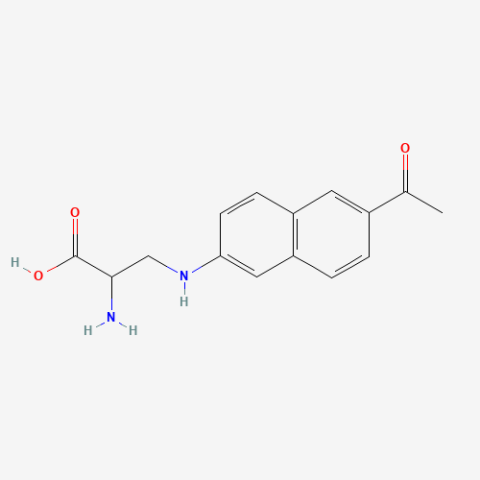
|
Highly environmentally sensitive fluorescent probe | Published: Under Review |
| Azidohomoalanine | 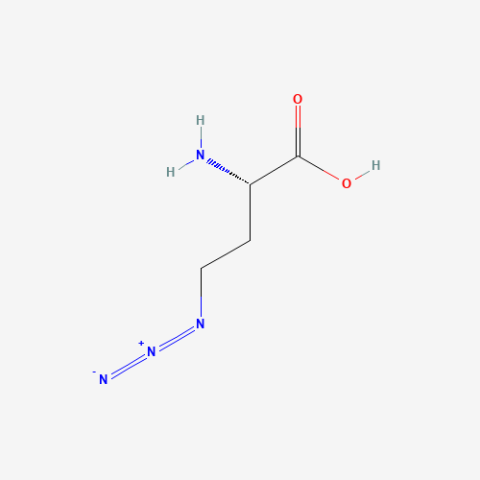
|
click chemistry, BONCAT (Bioorthogonal non-canonical amino-acid tagging) proteomics | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| Azidonorleucine | 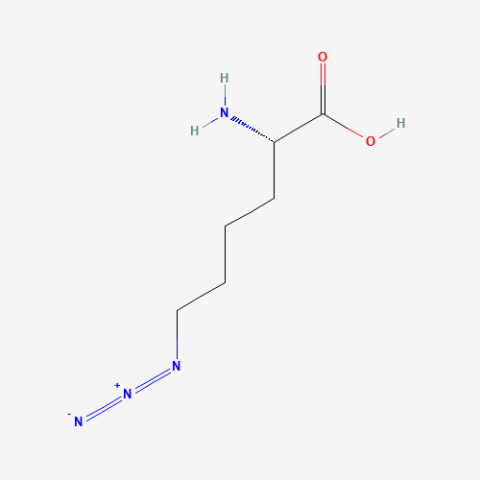
|
Biorthogonal Ligation, Click Chemistry labeling with fluorescence or affinity labels. Specifically used for cell-specific proteomics studies using "bioorthogonal noncanonical amino acid tagging" (BONCAT) proteomics. Contrasts with Azidohomoalanine which does not allow cell-specific studies. | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| DansylAla | 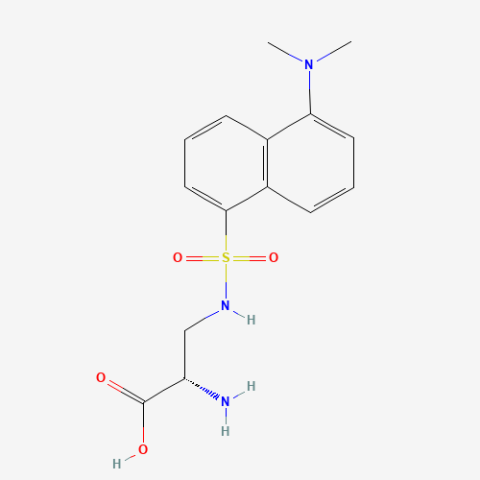
|
Fluorescent amino acid | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| endo-BCN-L-Lysine | 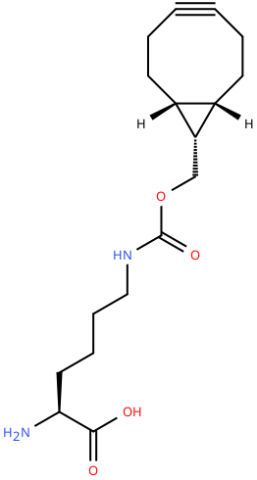
|
Reactive handle for SPAAC | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| exoBCN-L-Lysine | 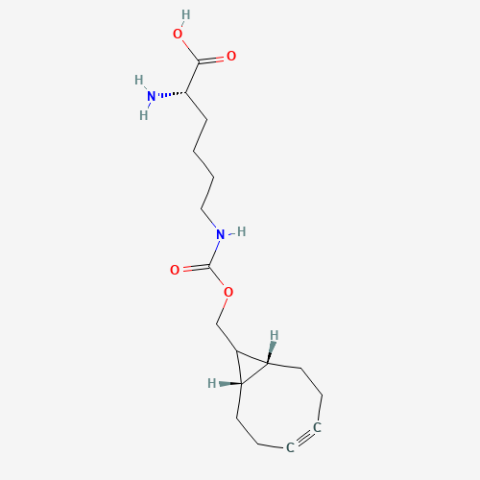
|
Reactive handle for SPAAC | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| l-Cys-e-Lys | 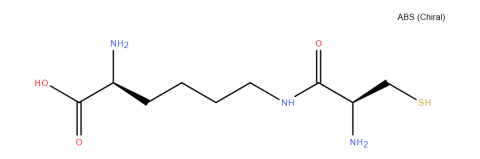
|
Condenses with 2-cyanobenzothiazole for protein modification. | Published: Under Review |
| N6-(Benzyloxycarbonyl)-L-lysine (Z-Lys) | 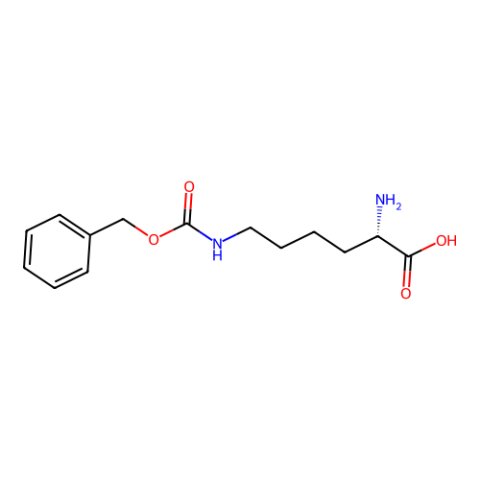
|
n/a | Published: Fully Reviewed |
| N6-Trifluoroacetyl-L-lysine | 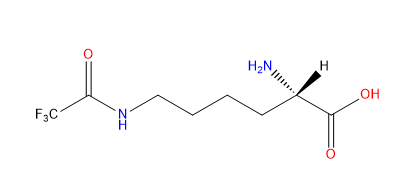
|
They are used for sites specifically studying post-translational modification acetylation events on particular lysine residues. Also be used as an F19 NMR probe. | Published: Under Review |